Initial setup¶
Here are three ways to practice the examples featured in this tutorial.
Google Colab - Online interpreter/notebook (Most convenient)¶
For each chapter, I've created a Google Colab notebook. It is based on Jupyter notebooks, which allows text and executable code to co-exist.
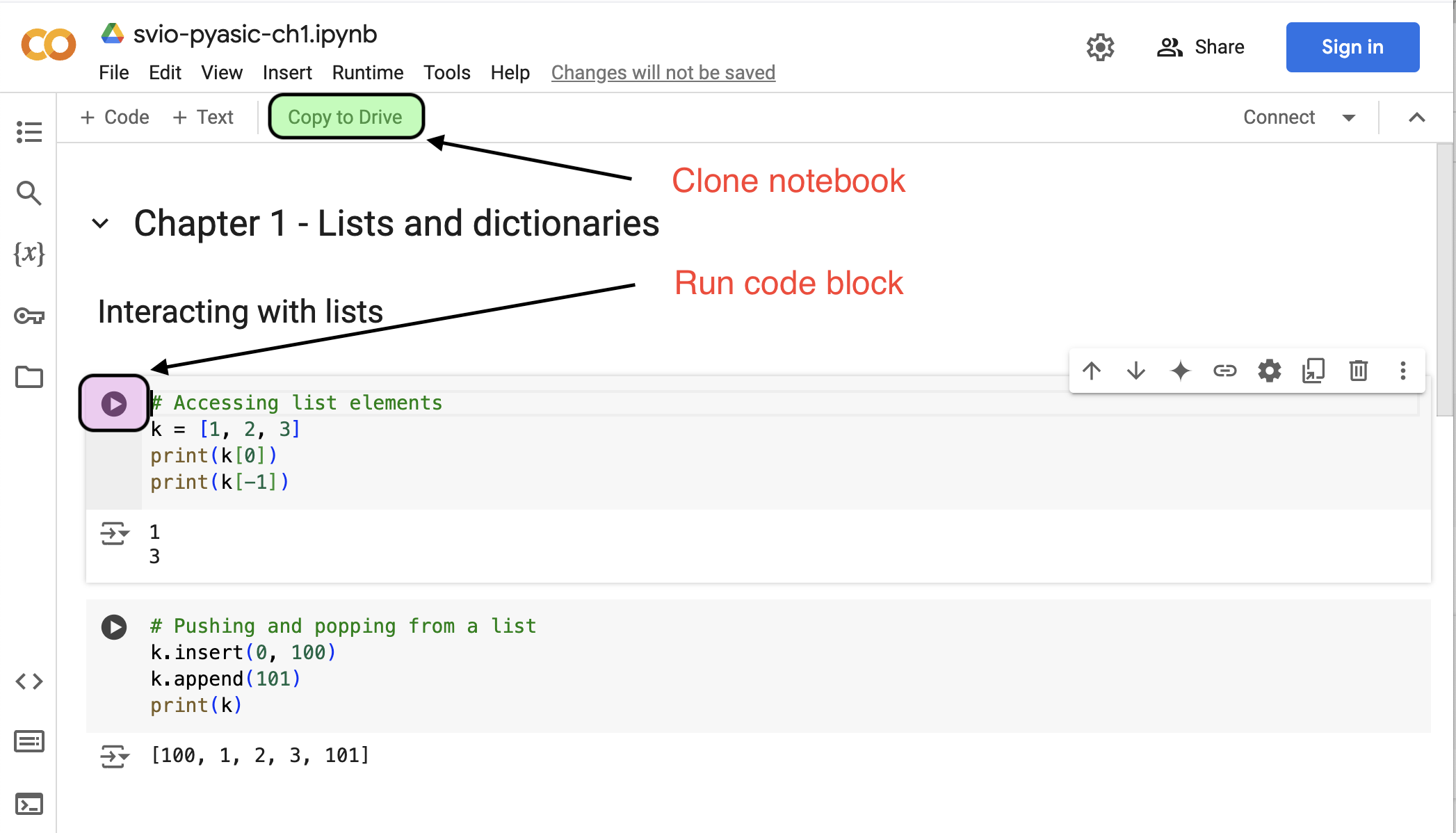
- Here is the link to Chapter 1 Google Colab
- Login with your gmail account, and click on the Copy to Drive button.
- Simply click the button on a code block to execute it.
- Edit and play around with each code block
Linux or MacOS (Preferred method)¶
- If you are a student or a working professional, you typically have access to a Linux machine through SSH/Putty or VNC.
- This is the preferred method because you will be learning to write Python code in the same environment where you are working with SystemVerilog code.
- You can launch Python by entering
python3in your Linux terminal. This also works for MacOS. - This is the method used for the code in this tutorial. Here is an example of what you will see when you enter
python3on a Linux terminal.
% python3
Python 3.9.6 (default, Oct 4 2024, 08:01:31)
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> hex(500)
'0x1f4'
>>> '/'.join(['user', 'path', 'dir'])
'user/path/dir'VS Code¶
VS Code is, arguable, the most popular IDE at the moment. This will allow you to follow the tutorial from your Windows or MacOS PC.
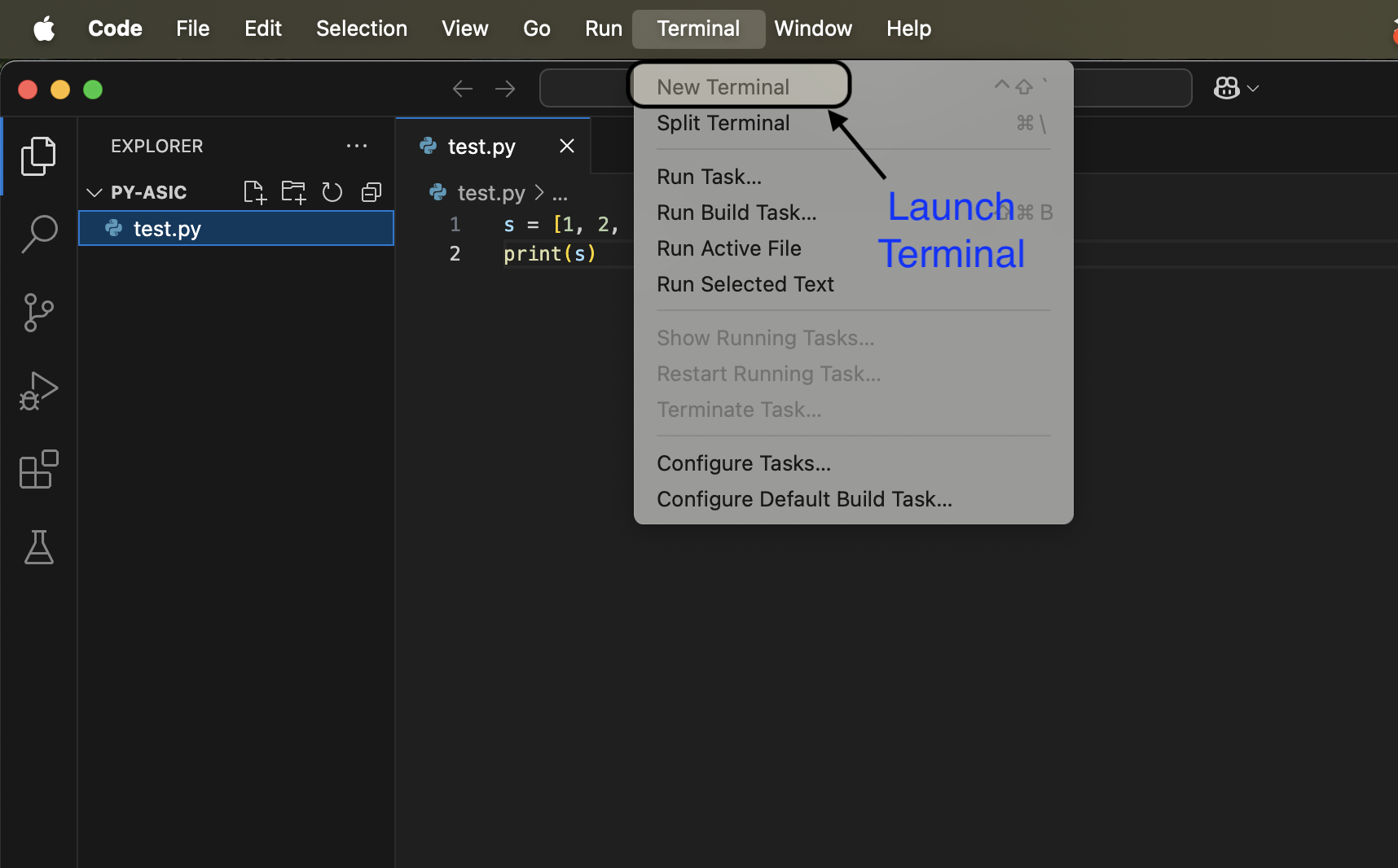
- Download VS Code
- Create a new file and name it
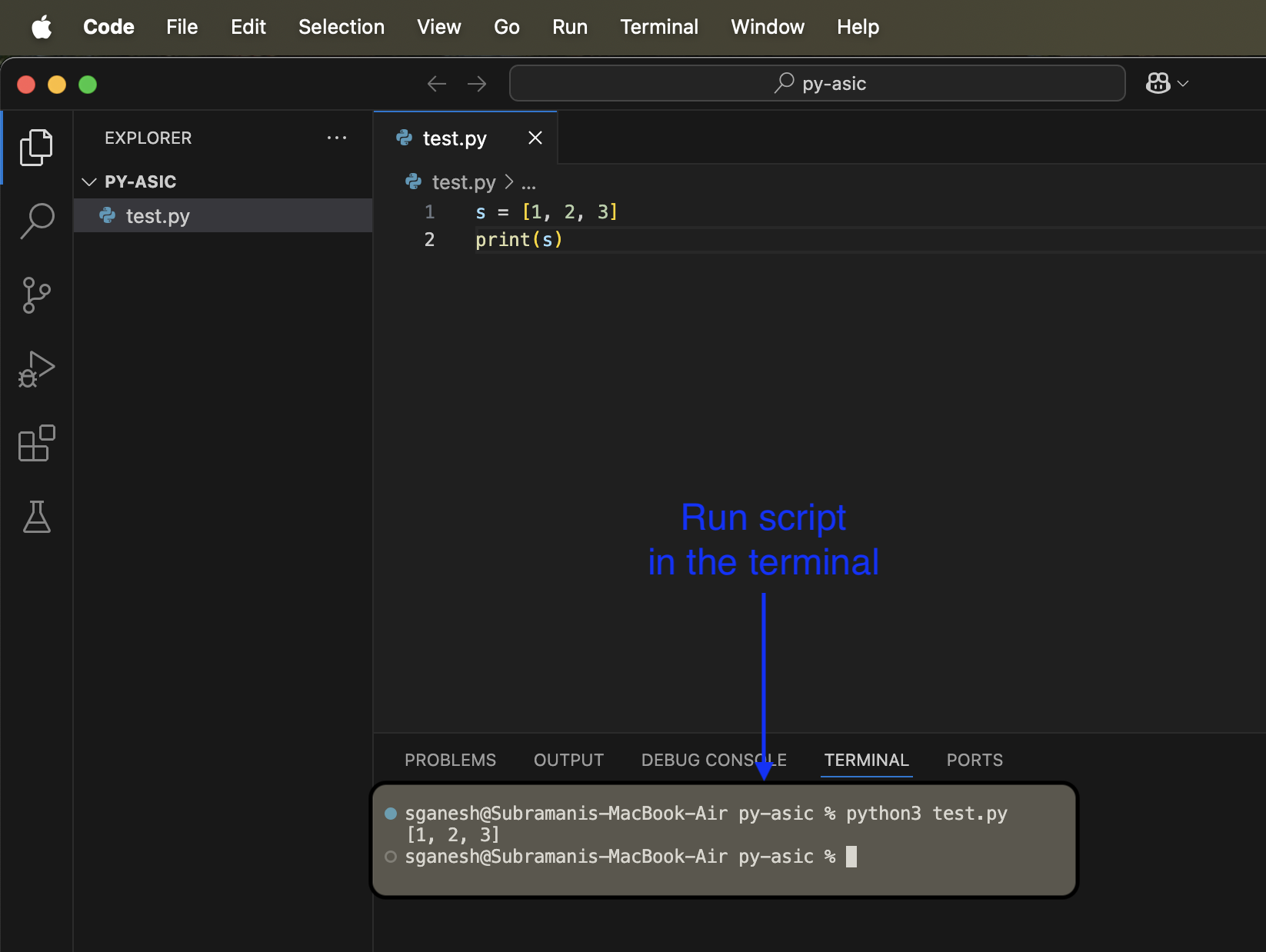
test.py - To run this python script, launch a terminal
- Type
python3 test.pyinto it
Read this next¶
Table of contents Chapter 1: Lists and dictionaries

